Reaction: propionyl-CoA + CO2 + ATP <=> D-methylmalonyl-CoA + ADP + orthophosphate
- in pathway: Propionyl-CoA catabolism
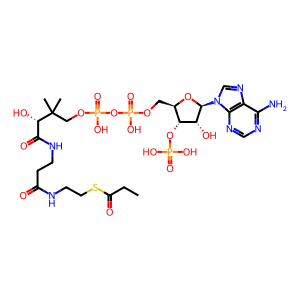
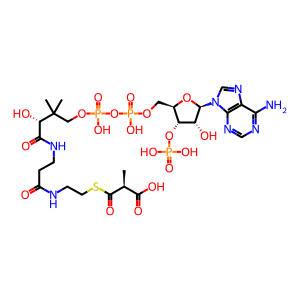
Propionyl CoA carboxylase in the mitochondrial matrix catalyzes the reaction of propionyl-CoA, CO2, and ATP to form D-methylmalonyl-CoA, ADP, and orthophosphate. The active form of the enzyme is a heteromultimer, probably consisting of six alpha subunits each bound to a biotin molecule and six beta subunits (Kaziro et al. 1961; Kalousek et al. 1980; Fenton et al. 2001). Both alpha and beta subunits are posttranslationally modified to remove amino-terminal mitochondrial import sequences (Stadler et al. 2005).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Pi [mitochondrial matrix]
ADP [mitochondrial matrix]
MEMA-CoA [mitochondrial matrix]
PROP-CoA [mitochondrial matrix]
ATP [mitochondrial matrix]
CO2 [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-71031
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
propionyl-CoA
ATP(4-)
carbon dioxide
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydrogenphosphate
ADP(3-)
(S)-methylmalonyl-CoA
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-71031