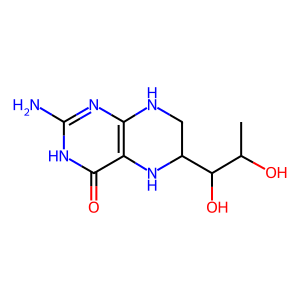
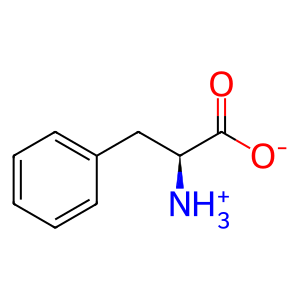
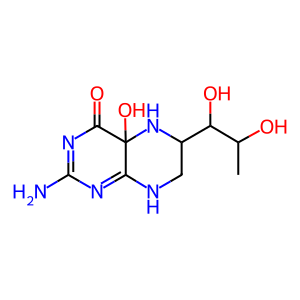
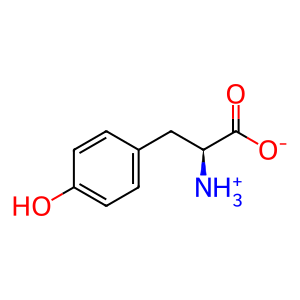
Reaction: PAH:Fe2+ tetramer hydroxylates L-Phe to L-Tyr
- in pathway: Phenylalanine metabolism
Inactivating mutations of cytosolic phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) block the normal reaction of phenylalanine, molecular oxygen and tetrahydrobiopterin to form tyrosine, water, and 4 alpha-hydroxytetrahydrobiopterin. Excess phenylalanine accumulates as a result, driving the formation of abnormally high levels of phenylpyruvate, and phenyllactate (Guldberg et al. 1996; Mitchell et al. 2011) in reactions not annotated here.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
4aOH-BH4 [cytosol]
L-Tyr [cytosol]
BH4 [cytosol]
L-Phe [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-71118
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobiopterin
L-phenylalanine zwitterion
dioxygen
Reaction output - small molecules:
4a-hydroxytetrahydrobiopterin
L-tyrosine zwitterion
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-71118