Reaction: GUCYs converts GTP to cGMP
The basal, "dark" levels of cGMP are restored as part of the recovery of light response by membrane guanylyl cyclases (GUCYs). Two variants, GUCY2D (Shyjan et al. 1992) and GUCY2F (Lowe et al. 1995), mediate the synthesis of cGMP from GTP. Unlike other membrane guanylyl cyclases, the rod types are not receptors for extracellular substances. Instead, GUCYs are regulated intracellularly by guanylyl cyclase activating proteins (GCAPs), this regulation being the most important negative feedback mechanism triggered by Ca2+ in light. There are three GCAPs in humans; GUCA1A, GUCA1B and GUCA1C (Subbaraya et al. 1994, Surguchov et al. 1997, Haeseleer et al. 1999). GCAPs are Ca2+ binding proteins. When Ca2+ concentration is high (in the "dark" condition), GCAPs bind Ca2+ and inhibit GUCYs. Conversely, when Ca2+ concentration is low (as in a light response), GCAPs release Ca2+ and bind Mg2+ in its place. With Mg2+ bound, GCAPs stimulate GUCY activity by an order of magnitude. This negative feedback operates rapidly to limit the amplitude and duration of the single photon response and to dampen the effects of spontaneous PDE activations. Mutations in GUCYD can give rise to Leber's congenital amaurosis or to cone-rod dystrophy (https://sph.uth.edu/retnet/).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
PPi [cytosol]
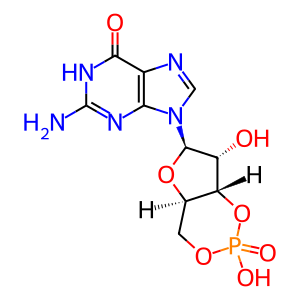
cGMP [cytosol]
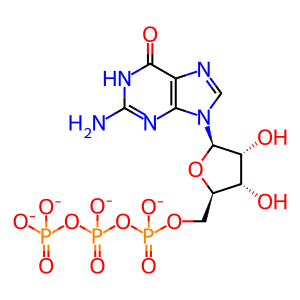
GTP [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-74885
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
GTP(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
diphosphate(3-)
3',5'-cyclic GMP
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-74885