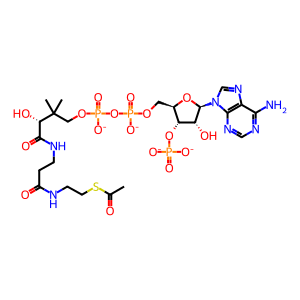
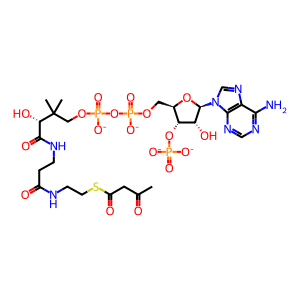
Reaction: ACAT2 condenses 2 Ac-CoA to form ACA-CoA
- in pathway: Cholesterol biosynthesis
Three human enzymes can utilise ketone bodies for energy production. Two mitochondrial enzymes function in ketolysis whereas a cytosolic enzyme is implicated in cytosolic cholesterol biosynthesis. Cytosolic acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase tetramer (ACAT2 tetramer) (Song et al. 1994) catalyses the condensation of two acetyl-CoA (Ac-CoA) molecules to form acetoacetyl-CoA (ACA-CoA). This is the first step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol (Fukao et al. 1997).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
ACA-CoA [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
CoA-SH [cytosol]
Ac-CoA [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8848215
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
acetyl-CoA(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
acetoacetyl-CoA(4-)
water
coenzyme A(4-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8848215