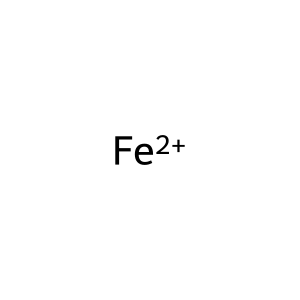Reaction: RNA demethylases demethylate N6-methyladenosine RNA
- in pathway: Reversal of alkylation damage by DNA dioxygenases
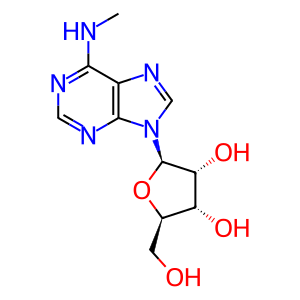
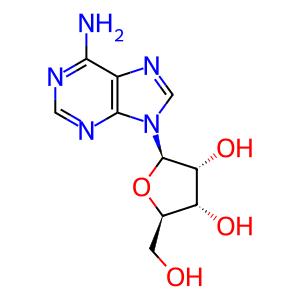
Fe2+- and oxoglutarate-dependent ALKB oxygenase family members are able to oxidatively demethylate alkylated DNA and RNA, thereby repairing them. The family members alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase FTO (FTO) and RNA demethylase ALKBH5 (ALKBH5) localise to the nucleus and can both specifically demethylate N(6)-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA, the most abundant internal modification of messenger RNA (mRNA) in higher eukaryotes (Han et al. 2010, Jia et al. 2011, Xu et al. 2014). FTO contributes to the regulation of the global metabolic rate, energy expenditure and energy homeostasis and is associated with body mass index (BMI) (Dina et al. 2007, Frayling et al. 2007, Zhang et al. 2015; reviews - Zhao et al. 2014, Merkestein & Sellayah 2015). ALKBH5 could play a role in spermatogenesis. Alkbh5-deficient male mice have increased N6-methyladenosine in mRNA and are characterised by impaired fertility (Zheng et al. 2013).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
adenosine [nucleoplasm]
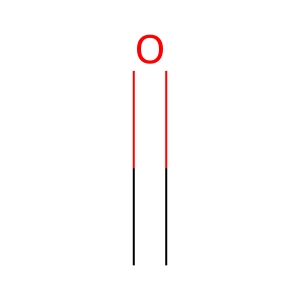
CH2O [nucleoplasm]
CO2 [nucleoplasm]
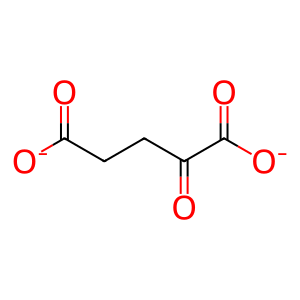
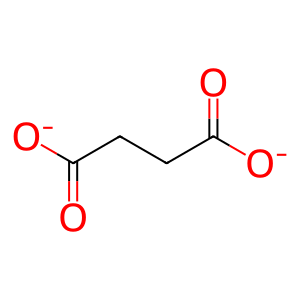
SUCCA [nucleoplasm]
N6-methyladenosine [nucleoplasm]
2OG [nucleoplasm]
Fe2+ [nucleoplasm]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8857692
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
N(6)-methyladenosine
2-oxoglutarate(2-)
iron(2+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
adenosine
formaldehyde
carbon dioxide
succinate(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8857692