Reaction: RGGT binds the RAB-binding subunit
- in pathway: RAB geranylgeranylation
The catalytic dimer of RGGTA and B interacts with RAB-escorting proteins 1 or 2 (CHM and CHML, also known as REP-1 and REP-2) to form a functional trimeric RAB geranylgeranyl transferase complex that is capable of binding and geranylgeranylating newly synthesized RAB proteins (Baron and Seabra, 2008; reviewed in Leung et al, 2006; Gutkowska and Swiezewska, 2012). There are two models for the formation of a functional enzyme:substrate complex. In the classical model, unprenylated RAB first binds to REP and is subsequently presented to the catalytic subunits of the GGTase. Incorporation of geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) strengthens the interaction between enzyme and substrate (Andres et al, 1993; Thoma et al, 2001a). In the alternate route, which is depicted in this pathway, RGGTA and RGGTB first bind to REP in a GGPP-dependent manner in the absence of the RAB substrate. Unprenylated RABs then bind to the fully formed GGTase for geranylgeranylation (Thoma et al, 2001b; Baron and Seabra, 2008).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
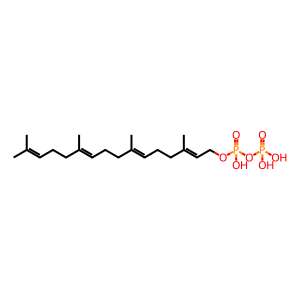
geranylgeranyl diphosphate [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8870465
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
2-trans,6-trans,10-trans-geranylgeranyl diphosphate
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8870465