Reaction: RGGT geranylgeranylates RAB proteins
- in pathway: RAB geranylgeranylation
RAB geranylgeranyltransferase (GGTase) recognizes and geranylgeranylates cysteine residues in -CXCX, -CCXX or -XXCC motifs in the C-termini of RAB proteins. Most RAB proteins are doubly geranylgeranylated, most likely in a sequential fashion, but some are only singly modified (Baron and Seabra, 2008; Farnsworth et al 1994; Wilson et al, 1996; Overmeyer et al, 2000; Khosravi-Far et al, 1991; Joberty et al, 1993; Catherman et al, 2013; Leung et al, 2007; Maurer-Stroh et al, 2007). In most cases, geranylgeranylation is required for proper localization and function of the RAB proteins. After geranylgeranylation, RABs remain associated with the RAB escort protein CHM or CHML, which dissociates when the GTPase reaches its target membrane (Alexandrov et al, 1994; Seabra et al, 1996; Shen and Seabra, 1996). Release of the geranylgeranyl RAB:CHM complex from the catalytic subunits is promoted by the binding of additional GGPP to the enzyme (Baron and Seabra, 2008). Once prenylated, RABs cycle between active GTP bound forms that are membrane associated, and inactive GDP bound forms that are cytosolic and associated with RAB GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI) proteins. Conversion between these states is governed by the activities of guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs), which promote the exchange of GDP for GTP, and GTPase activating proteins (GAPs), which stimulate the intrinsic GTPase activity of RABs (Ullrich et al, 1993; Soldati et al, 1994; reviewed in Wandinger-Ness and Zerial, 2014; Stenmark, 2009).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
PPi [cytosol]
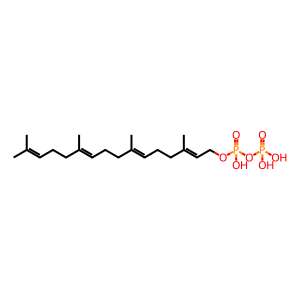
geranylgeranyl diphosphate [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8870469
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
2-trans,6-trans,10-trans-geranylgeranyl diphosphate
Reaction output - small molecules:
diphosphate(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8870469