Reaction: RAB13 GEFs exchange GTP for GDP on RAB13
- in pathway: RAB GEFs exchange GTP for GDP on RABs
RAB13 is involved in the trafficking of proteins in the biosynthetic and endosomal recycling pathways and contributes to processes such as tight junction formation and cell adhesion, GLUT 4 transport, angiogenesis, reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, cell migration and cellular proliferation (Marzesco et al, 2002; Kohler et al, 2004; Morimoto et al, 2005; Terai et al, 2006; Yamamura et al, 2008; Nokes et al, 2008; Sun et al, 2010; Sakane et al, 2010; Sun et al, 2012; Nishikimi et al, 2014; Sun et al, 2016). These processes are often misregulated in cancer cells, and consistent with this, RAB13 has been implicated as a driver of cancer progression and is upregulated in multiple cancer types (Mahadevan et al, 2005; Li et al, 2014; Ioannou et al, 2015; reviewed in Iaonnou and McPherson, 2016). RAB13 is activated at the plasma membrane by its GEFs, DENND1C and DENND2B (also known as ST5), and may also be activated at other sites at lower levels (Yoshimura et al, 2010; Marat et al, 2012; Nishikimi et al, 2014; Ioannou et al, 2015; reviewed in Ishida et al, 2016). In this reaction, GDI and CHM proteins are depicted keeping the inactive, GDP-bound RAB13 soluble, in accordance with the classic view of the RAB cycle. A recent paper, however, provides evidence that in the case of RAB13, inactive RAB13:GDP traffics on vesicles, tethered by interaction with vesicle-bound proteins, and resists GDI-dependent extraction from membranes (Ioannou et al, 2016).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
GDP [cytosol]
GTP [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8876615
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
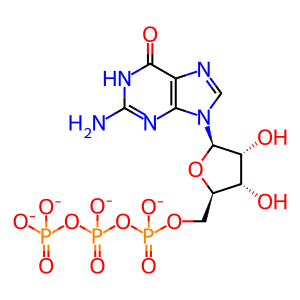
GTP(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
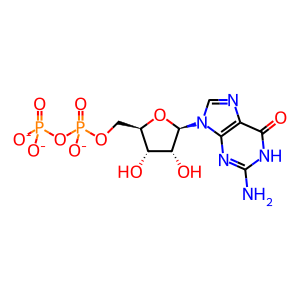
GDP(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8876615