Reaction: CARNMT1 methylates CARN to Anserine
- in pathway: Histidine catabolism
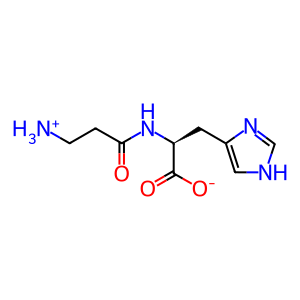
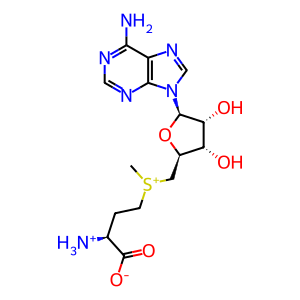
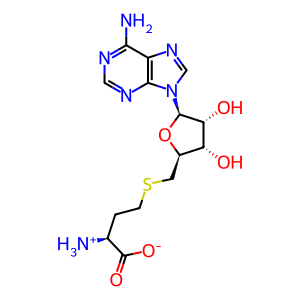
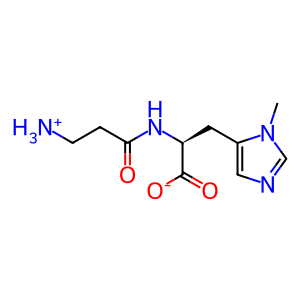
Anserine (Beta-alanyl-N(Pi)-methyl-L-histidine) is a methylated derivative of carnosine (Beta-alanyl-L-histidine) and an abundant constituent of vertebrate skeletal muscles (Boldyrev et al. 2013). It has been suggested to serve as a proton buffer and radical scavenger. The formation of anserine is catalyzed by carnosine N-methyltransferase (CARNMT1), which transfers a methyl group from S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) onto the nitrogen atom (Pi) of L-histidine residue in carnosine (Drozak et al. 2015). While CARNMT1 produces anserine in mammals, a similar reaction is catalysed by a different enzyme (carnosine N-methyltransferase 2) in birds and reptiles (Drozak et al. 2013).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
AdoHcy [cytosol]
Anserine [cytosol]
CARN [cytosol]
AdoMet [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8876789
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
carnosine zwitterion
S-adenosyl-L-methionine zwitterion
Reaction output - small molecules:
S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine zwitterion
anserine zwitterion
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8876789