Reaction: AHR:2xHSP90:AIP:PTGES3 binds TCDD
- in pathway: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor signalling
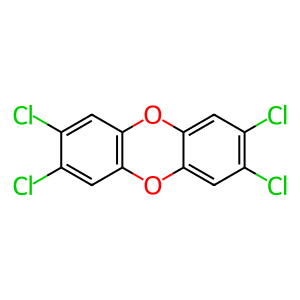
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) is a ligand-activated transcription factor that can control the expression of a diverse set of genes. Two major types of environmental compounds can activate AHR signaling: halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons such as 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) such as benzo(a)pyrene. Unliganded AHR forms a complex in the cytosol with two copies of 90kD heat shock protein (HSP90AB1) (Forsythe et al. 2001), one X-associated protein (AIP) (Meyer et al. 1998), and one p23 molecular chaperone protein (PTGES3) (Nguyen et al. 2012, Beischlag et al. 2008). Here, the binding of TCDD is shown.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
TCDD [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8936849
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzodioxine
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8936849