Reaction: ALOX15 oxidises DHA to 17(S)-Hp-DHA
- in pathway: Biosynthesis of DHA-derived SPMs
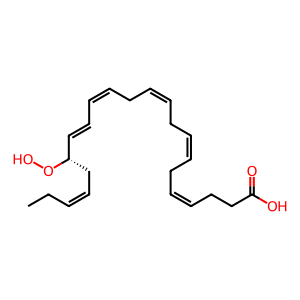
In the absence of aspirin in human whole blood, isolated leukocytes and glial cells, 15-lipoxygenase (ALOX15) can oxygenate docosahexanoic acid (DHA) (Kim et al. 1990) to the 17(S) epimer 17(S)-hydroperoxy-docosahexanoic acid (17(S)-Hp-DHA) (Hong et al. 2003). This intermediate leads to the production of 17(S) epimer D-resolvins (as opposed to aspirin-triggered 17(R) epimer D-resolvins), as well as being the precursor for protectins and the proposed precursor for the production of protectin conjugates in tissue regeneration (PCTRs) and resolvin conjugates in tissue regeneration (RCTRs) (Dalli et al. 2015, Ramon et al. 2016).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
17(S)-Hp-DHA [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
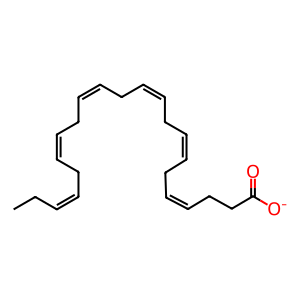
DHA [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9020275
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
dioxygen
(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)-docosahexaenoate
Reaction output - small molecules:
(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,15E,17S,19Z)-17-hydroperoxydocosahexaenoic acid
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9020275