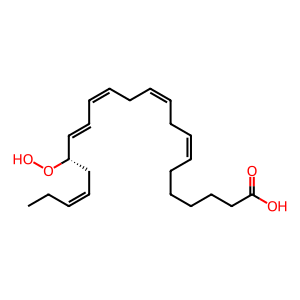
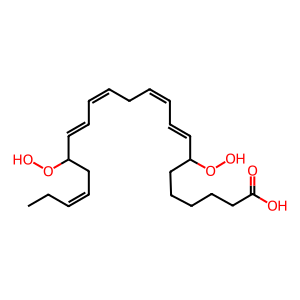
Reaction: ALOX5 oxidises 17(S)-Hp-DPAn-3 to 7,17-diHp-DPAn-3
- in pathway: Biosynthesis of DPAn-3-derived protectins and resolvins
In an alternative route to the production of protectins PD1n-3DPA and PD2n-3DPA, 17(S)-hydroperoxy-docosapentaenoic acid (17(S)-Hp-DPAn-3) can be further oxygenated by a lipoxygenase to form 7,17-dihydroperoxy-docosapentaenoic acid (7,17-diHp-DPAn-3) (Dalli et al. 2013). Although this is a proposed biosynthetic route, it is assumed DPAn-3-derived SPMs follow a similar synthesis route to DHA- and EPA-derived SPMs therefore the lipoxygenase could be the dual-functional 5-lipoxygenase (ALOX5).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
7,17-diHp-DPAn-3 [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
17(S)-Hp-DPAn-3 [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9025996
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
dioxygen
(7Z,10Z,13Z,15E,17S,19Z)-17-hydroperoxydocosapentaenoic acid
Reaction output - small molecules:
(8E,10Z,13Z,15E,19Z)-7,17-bis(hydroperoxy)docosapentaenoic acid
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9025996