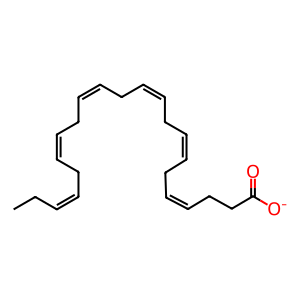
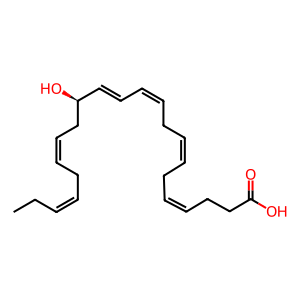
Reaction: CYPs hydroxylate DHA to 14(R)-HDHA
- in pathway: Biosynthesis of maresin-like SPMs
Using human leukocytes and platelets, Hong et al. found that incubating docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) with a mixture of human cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP1A2, 2C8, 2C9, 2D6, 2E1 and 3A4) formed 14(R)-hydroxy-docsosahexaenoic acid (14(R)-HDHA), the precursor to maresin-like mediator 2 (MaR-L2) (Hong et al. 2014). There is no data to indicate which one or ones of these CYPs mediate this event under physiological conditions. CYP inhibition diminishes the formation of 14(R)-HDHA, confirming CYP determines 14(R)-hydroxylation (Hong et al. 2014). The CYP mixture also formed 22-hydroxy-docosahexaenoic acid (22-HDHA) by ω-oxidation (not shown here). Although the CYP mixture also catalysed the formation of 14(S)-HDHA, the amount formed is minor compared to that formed by 12-lipoxygenase (Hong et al. 2014).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H2O [cytosol]
NADP+ [cytosol]
14(R)-HDHA [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
DHA [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9027043
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hydron
dioxygen
NADPH(4-)
(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)-docosahexaenoate
Reaction output - small molecules:
water
NADP(3-)
(14R)-HDoHE
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9027043