Reaction: CYP4 ω-oxidises 14(R)-HDHA to MaR-L2
- in pathway: Biosynthesis of maresin-like SPMs
Cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes are thought to ω-hydroxylate (position 22) 14(R)-hydroxy-docosahexaenoic acid (14(R)-HDHA) to 14(R),22-dihydroxy-docosahexaenoic acid, namely maresin-like mediator 2 (MaR-L2) (Hong et al. 2014). CYP inhibition was found to decrease the amount of MaR-L2 formed (Hong et al. 2014). The exact CYP responsible for MaR-L2 formation is unknown but is likely to be a member of the CYP4 family as those enzymes mediate the ω-hydroxylation of fatty acids and eicosanoids (Kikuta et al. 2002). Diabetes results in delayed- or non-healing of wounds and is associated with impaired macrophage function (Brem & Tomic-Canic 2007). Leukocytes and platelets play critical roles in wound healing by mechanisms as yet unknown. Maresin-like mediators MaR-L1 and Mar-L2 are produced by leukocytes and platelets and have been shown (in vitro) to restore reparative functions of diabetic macrophages in wounds (Hong et al. 2014).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H2O [cytosol]
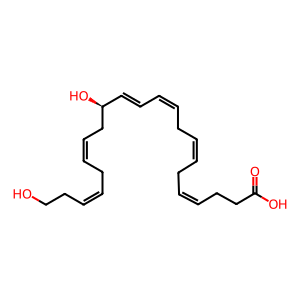
MaR-L2 [cytosol]
NADP+ [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
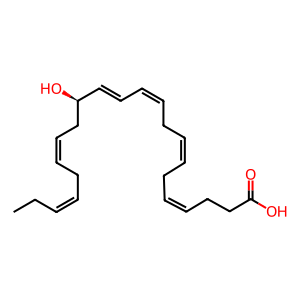
14(R)-HDHA [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9027044
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hydron
dioxygen
NADPH(4-)
(14R)-HDoHE
Reaction output - small molecules:
water
(4Z,7Z,10Z,12E,14R,16Z,19Z)-14,22-dihydroxydocosahexaenoic acid
NADP(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9027044