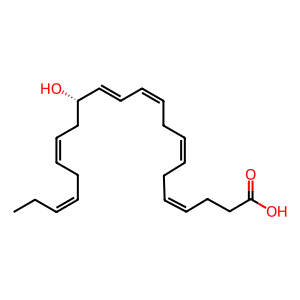
Reaction: CYP2E1 oxidises 14(S)-HDHA to 14(S),21(R)-diHDHA and 14(S),21(S)-diHDHA
- in pathway: Biosynthesis of maresin-like SPMs
In macrophages, cytochrome P450s (CYPs) are likely to 21-hydroxylate 14(S)-hydroxy-docosahexaenoic acid (14(S)-HDHA) to 14(S),21(R)-dihydroxy-docosahexaenoic acid (14(S),21(R)-diHDHA) and 14(S),21(S)-diHDHA (Lu et al. 2010, Tian et al. 2011a, 2011b). In human skin, CYP1A1, 2B6/7, 2E1, 3A4/7 and 3A5 proteins have been identified and shown to possess catalytic activities (Swanson 2004). CYP2E1 is able to generate 19-hydroxyleicosatetraenoic acid, an ω-1 hydroxylation intermediate of arachidonic acid (Laethem et al. 1993) therefore, it might also ω-1 hydroxylate 14(S)-HDHA in human skin.
14(S),21(R)-diHDHA was shown to counteract the diabetic impairment of macrophage pro-healing functions in an autocrine/paracrine fashion, enhancing wound healing (Lu et al. 2010, Tian et al. 2011a, 2011b).
14(S),21(R)-diHDHA was shown to counteract the diabetic impairment of macrophage pro-healing functions in an autocrine/paracrine fashion, enhancing wound healing (Lu et al. 2010, Tian et al. 2011a, 2011b).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H2O [cytosol]
NADP+ [cytosol]
14(S)-HDHA [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9027302
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
(14S)-HDoHE
hydron
dioxygen
NADPH(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
water
NADP(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9027302