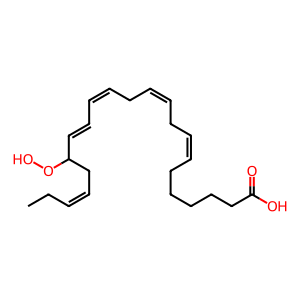
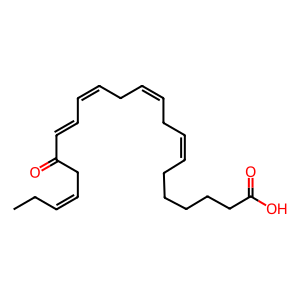
Reaction: Dehydrogenase dehydrogenates 17-HDPAn-3 to 17-oxo-DPAn-3
- in pathway: Biosynthesis of electrophilic ω-3 PUFA oxo-derivatives
In activated macrophages, an unknown dehdyrogenase abstracts hydrogen from 17-hydroxy-docosapentaenoic acid (17-HDPAn-3) to form the electrophilic oxo (EFOX) derivative 17-oxo-DPAn-3 (Groeger et al. 2010). Potential candidates are cellular dehydrogenases such as 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases (3α-HSDs), which can convert 13- and 17-HDHA into corresponding EFOXs in the presence of NAD(P)+ in vitro(supplementary data, Groeger et al. 2010) or 5- and 15-hydroxyeicosanoid dehydrogenases (5- and 15-HEDH, Wendell et al. 2015), which convert LOX products to 5-and 15-oxoETE (Erlemann et al. 2007). 17-oxo-DPAn-3 can act as a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ) agonist and inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokine and nitric oxide production, confirming its anti-inflammatory actions (Groeger et al. 2010).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
17-oxo-DPAn-3 [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
17-HDPAn-3 [cytosol]
NADP+ [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9027600
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
(7Z,10Z,13Z,15E,19Z)-17-hydroperoxydocosapentaenoic acid
NADP(3-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
(7Z,10Z,13Z,15E,19Z)-17-oxodocosapentaenoic acid
NADPH(4-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9027600