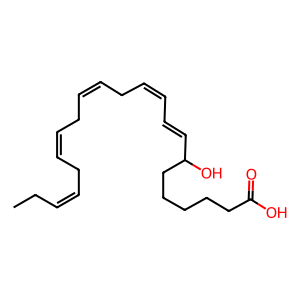
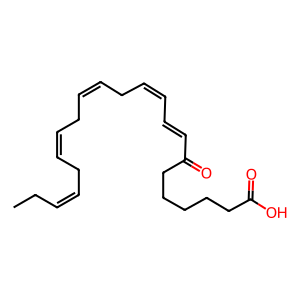
Reaction: 5-HEDH dehydrogenates 7-HDPAn-3 to 7-oxo-DPAn-3
- in pathway: Biosynthesis of electrophilic ω-3 PUFA oxo-derivatives
In neutrophils, 5-hydroxyeicosanoid dehydrogenase (5-HEDH) activity is localised in the microsomal fraction and requires NADP+ as a cofactor to oxidise 7-hydroxy-ω-3-docosapentaenoic acid (7-HDPAn-3) to 7-oxo-ω-3-docosapentaenoic acid (7-oxo-DPAn-3) (Patel et al. 2009, Cipollina et al. 2014). Although 5-HEDH activity has been found in a wide range of intact cells and in crude microsome preparations, the enzyme has not yet been purified, its structure is unknown, and the gene that encodes it remains to be identified. Dietary EPA supplementation significantly increases the formation of 7-oxo-DPAn-3 that transduces anti-inflammatory actions rather than suppressing production of pro-inflammatory AA metabolites (Cipollina et al. 2014).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
7-oxo-DPAn-3 [cytosol]
7-HDPAn-3 [cytosol]
NADP+ [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9027625
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
(8E,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)-7-hydroxydocosapentaenoic acid
NADP(3-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
NADPH(4-)
(8E,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)-7-oxodocosapentaenoic acid
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9027625