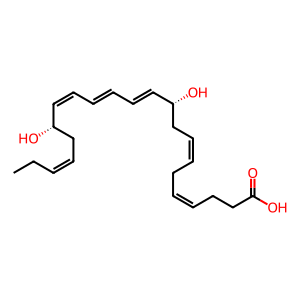
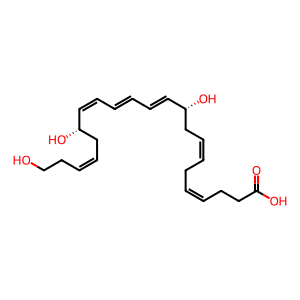
Reaction: CYP1, CYP2 hydroxylate (N)PD1 to 22-OH-(N)PD1
- in pathway: Biosynthesis of protectins
Protectin D1, identified as (N)PD1 (N signifies neuroprotectin when produced in neural tissues), is a natural product derived from docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) through the actions of 15 lipoxygenase followed by enzymatic hydrolysis by an unidentified hydrolase. (N)PD1 is one of the specialized proresolving mediators (SPMs) that show potent anti inflammatory and pro resolving actions (Molfino et al. 2017, Balas & Durand 2016). (N)PD1 has been the subject of many pharmacological studies for the development of potential new anti inflammatory drugs. The 22 hydroxylated metabolite of (N)PD1 (here signified as 22 OH (N)PD1) has been shown to exhibit potent pro resolving actions by inhibiting PMN chemotaxis in vivo with mice and in vitro with human cells and decreases pro inflammatory mediator levels in inflammatory exudates. These observations were comparable to those of its precursor (N)PD1 (Tungen et al. 2014). 22 OH (N)PD1 is most likely formed by the action of CYP1 monooxygenases, just like for some other SPMs (Divanovic et al. 2013).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H2O [cytosol]
NADP+ [cytosol]
22-OH-(N)PD1 [cytosol]
(N)PD1 [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9037761
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
protectin D1
hydron
dioxygen
NADPH(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
water
NADP(3-)
22-hydroxyprotectin D1
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9037761