Reaction: KDM8:Fe2+ hydroxylates an arginine residue of RCCD1
- in pathway: Protein hydroxylation
KDM8 (JMJC5 - JmjC domain-containing protein 5), active when bound to Fe2+, catalyzes the hydroxylation of an arginine residue of RCCD1 (RCC1 domain-containing protein 1). The subcellular location of this reaction under physiological conditions has not been determined; it is arbitrarily annotated as cytosolic.
KDM8, a member of the JmjC protein family, was originally assigned to the branch of the family that catalyzes histone lysine demethylation reactions. Structural studies have shown a closer resemblance to the protein hydroxylation branch of the family (Del Rizzo et al. 2012; Wang et al. 2013), a suggestion confirmed by in vitro studies with synthetic peptides (Wilkins et al. 2018). These studies identified RCCD1 as a likely hydroxylation target.
KDM8, a member of the JmjC protein family, was originally assigned to the branch of the family that catalyzes histone lysine demethylation reactions. Structural studies have shown a closer resemblance to the protein hydroxylation branch of the family (Del Rizzo et al. 2012; Wang et al. 2013), a suggestion confirmed by in vitro studies with synthetic peptides (Wilkins et al. 2018). These studies identified RCCD1 as a likely hydroxylation target.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
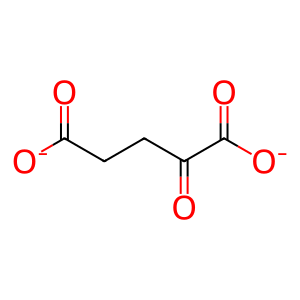
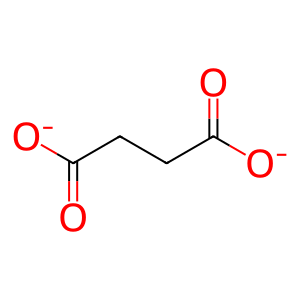
SUCCA [cytosol]
CO2 [cytosol]
2OG [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9629888
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
2-oxoglutarate(2-)
dioxygen
Reaction output - small molecules:
succinate(2-)
carbon dioxide
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9629888