Reaction: ASPH:Fe2+ hydroxylates an aspartate residue of F9
- in pathway: Protein hydroxylation
ASPH (aspartyl/asparaginyl beta-hydroxylase) 3-hydroxylates aspartate 110 of F9 (clotting factor IX). The active form of the human enzyme is inferred from studies of its bovine homolog to be a monomer complexed with Fe2+ and localized to the endoplasmic reticulum (Wang et al. 1991; Jia et al. 1992). Hydroxylated aspartate residues have been found in F9 and many other proteins with EGF domains (McMullen et al. 1983). The physiological role of this modification has not been determined. F9 has been chosen for annotation here because its reaction with ASPH has been characterized in vitro.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
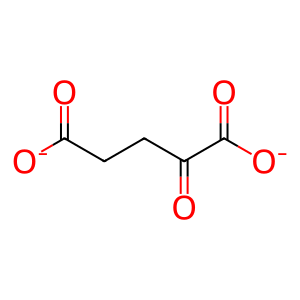
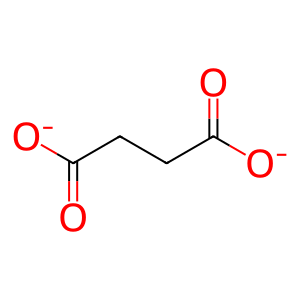
SUCCA [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
CO2 [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
O2 [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
2OG [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9631355
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
dioxygen
2-oxoglutarate(2-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
succinate(2-)
carbon dioxide
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9631355