Reaction: MLKL binds IP4, IP5 and IP6
- in pathway: Regulation of necroptotic cell death
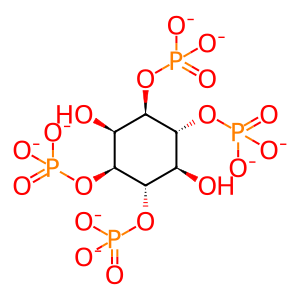
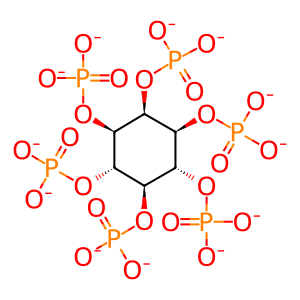
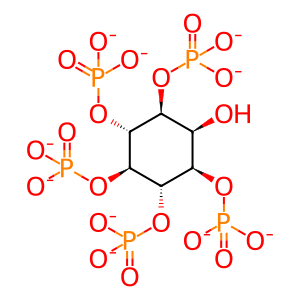
Metabolites of the inositol phosphate (IP) pathway I(1,3,4,6)P4, I(1,3,4,5,6)P5, and IP6 promote membrane permeabilization mediated by the pseudokinase mixed lineage kinase domain-like (MLKL) through directly binding the N‑terminal four-helical bundle (4HB) domain and dissociating its auto-inhibitory region (Dovey CM et al. 2018; McNamara DE et al. 2019). This is consistent with the findings that inositol polyphosphate kinases (IPK) IPMK and ITPK1 are essential regulators of MLKL-mediated necroptosis in a forward genetic screen performed with the human haploid cell line HAP1 (Dovey CM et al. 2018). Subsequent genetic deletion of IPK genes IPMK, ITPK1 and IPPK of the IP code metabolic pathway blocked MLKL-mediated necroptosis in human colon adenocarcinoma HT-29 cells (Dovey CM et al. 2018; McNamara DE et al. 2019). Activating IPs bind three sites on MLKL with affinity of 100-600 μM to destabilize contacts between the auto-inhibitory region and NED of MLKL. This liberates NED, promoting oligomerization and activation of MLKL (McNamara DE et al. 2019).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
I(1,3,4,6)P4 [cytosol]
IP6 [cytosol]
I(1,3,4,5,6)P5 [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9687638
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
myo-inositol 1,3,4,6-tetrakisphosphate(8-)
myo-inositol hexakisphosphate(12-)
myo-inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate(10-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9687638