Reaction: KDM5A demethylates histone H3 trimethyllysine-4 (H3K4me3)
The histone demethylase KDM5A (JARID1A, RBBP2, RBP2) demethylates trimethylated histone 3 lysine-4 (H3K4me3, lysine-5 of the preprotein) in in vitro and in embryonic stem cells (Christensen et al. 2007, Iwase et al. 2077, Klose et al. 2007) and is inferred to catalyze the same reaction in zygotes. KDM5A can processively remove all three methyl groups to yield unmethylated H3K4 (Christensen et al. 2007, Klose et al. 2007), however other studies showed demethylation of H3K4me3 to H3K4me2 and H3K4me1 (Iwase et al. 2007). In 2-cell embryos, nucleosomes contain a canonical distrubution of H3.1, H3.2, and H3.3 (inferred from mouse embryos). KDM5A and KDM5B are responsible for demethylating the broad regions of H3K4me3 that are inherited from oocytes (inferred from mouse embryos). The result is peaks of H3K4me3 at the 5' and 3' ends of genes.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
CH2O [nucleoplasm]
CO2 [nucleoplasm]
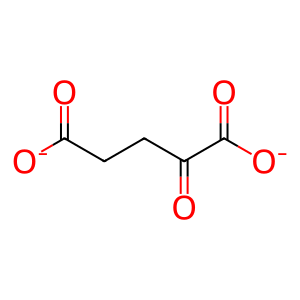
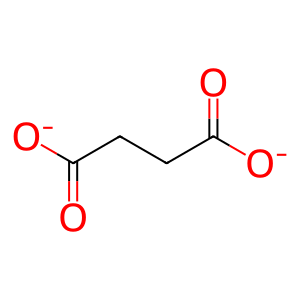
SUCCA [nucleoplasm]
2OG [nucleoplasm]
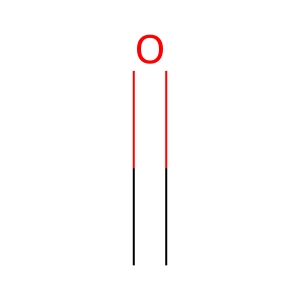
O2 [nucleoplasm]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9822467
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
2-oxoglutarate(2-)
dioxygen
Reaction output - small molecules:
formaldehyde
carbon dioxide
succinate(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9822467