Reaction: PLC beta-mediated PIP2 hydrolysis
- in pathway: Ca2+ pathway
Phospholipase C (PLC) isozymes are a group of related proteins that cleave the polar head group from inositol phospholipids, typically in response to signals from cell surface receptors. They hydrolyze the highly phosphorylated lipid phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) generating two products: inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3), a universal calcium-mobilizing second messenger, and diacylglycerol (DAG), an activator of protein kinase C. PLC-beta isoforms are regulated by heterotrimeric GTP-binding proteins. PLC-beta 1 and 3 are widely expressed, with the highest concentrations found in (differing) specific regions of the brain. PLC-beta 2 is expressed at highest levels in cells of hematopoeitic origin; it is involved in leukocyte signaling and host defense. PLC-beta 4 is highly concentrated in cerebellar Purkinje and granule cells, the median geniculate body, whose axons terminate in the auditory cortex, and the lateral geniculate nucleus, where most retinal axons terminate in a visuotopic representation of each half of the visual field.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
I(1,4,5)P3 [cytosol]
DAG [plasma membrane]
PI(4,5)P2 [plasma membrane]
I(1,4,5)P3 [cytosol]
DAG [plasma membrane]
PI(4,5)P2 [plasma membrane]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-398193
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
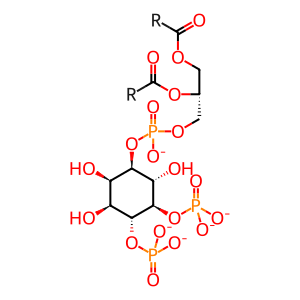
1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate(5-)
1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate(5-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
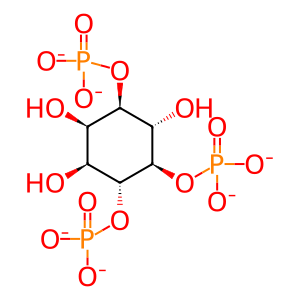
1D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate(6-)
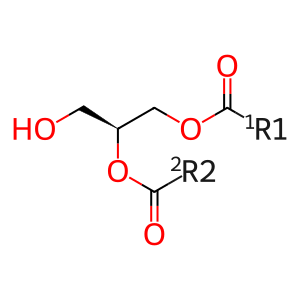
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol
1D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate(6-)
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-398193