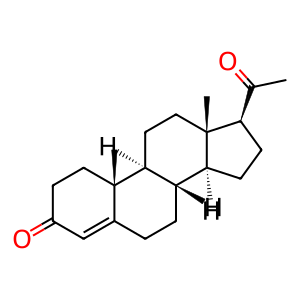
Reaction: Defective CYP21A2 does not 21-hydroxylate PROG
- in pathway: Defective CYP21A2 causes AH3
Steroid 21-hydroxylase (CYP21A2) specifically catalyses the 21-hydroxylation of steroids which is required for the adrenal synthesis of mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids. Defects in CYP21A2 can cause adrenal hyperplasia 3 (AH3; MIM:201910), a form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) where cortisol synthesis is defective. This results in increased ACTH levels, causing overproduction and accumulation of cortisol precursors, particularly 17-hydroxyprogesterone (17HPROG). The resultant excessive production of androgens causes virilization. The most severe form of CAH caused by CYP21A2 is known as salt-wasting (SW), which is due to complete or almost complete loss of enzymatic activity. CYP21A2 mutations causing SW include G292S, V237E, Q318*, W406*, E380D (Wedell et al. 1992, White et al. 1998, Robins et al. 2005, Wedell & Luthman 1993, Kirby-Keyser et al. 1997).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
P4 [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5601976
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
progesterone
hydron
dioxygen
NADPH(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5601976