Reaction: Defective CYP7B1 does not 7-hydroxylate 25OH-CHOL
- in pathway: Defective CYP7B1 causes SPG5A and CBAS3
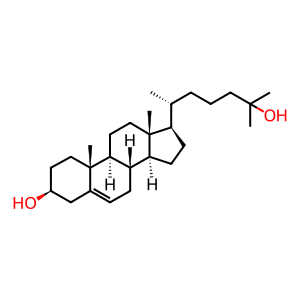
25-hydroxycholesterol 7-alpha-hydroxylase (CYP7B1) normally 7alpha-hydroxylates 25-hydroxycholesterol (25OH-CHOL) to cholest-5-ene-3beta,7alpha,25-triol (CHOL3b,7a,25TRIOL). Defects in CYP7B1 can cause spastic paraplegia 5A, autosomal recessive (SPG5A; MIM:270800), a neurodegenerative disorder characterised by a slow, gradual, progressive weakness and spasticity of the lower limbs (Tsaousidou et al. 2008). Mutations causing SPG5A include S363F, G57R, R417H, F216S, Y275*, F470I, G87V and T297A (Tsaousidou et al. 2008, Schule et al. 2009, Goizet et al. 2009, Arnoldi et al. 2012). Defects in CYP7B1 can also cause congenital bile acid synthesis defect 3 (CBAS3; MIM:613812), a disorder resulting in severe cholestasis, cirrhosis and liver synthetic failure. Hepatic CYP7B1 activity is undetectable (Setchell et al. 1998). A mutation causing CBAS3 is R388* (Setchell et al. 1998).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
25OH-CHOL [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5602885
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hydron
dioxygen
25-hydroxycholesterol
NADPH(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5602885