Reaction: Defective CYP1B1 does not 4-hydroxylate EST17b
- in pathway: Defective CYP1B1 causes Glaucoma
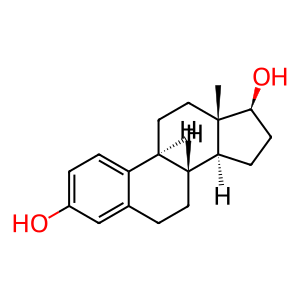
Cytochrome P450 1B1 (CYP1B1) can oxidise a variety of structurally unrelated compounds, including steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics as well as activating a range of procarcinogens. A specific substrate is the female sex hormone estradiol-17beta (EST17b) which is 4-hydroxylated to 4-hydroxyestradiol-17beta 4OH-EST17b) (Badawi et al. 2001). Defects in CYP1B1 can cause glaucoma disorders such as Glaucoma 3, primary congenital, A (GLC3A; MIM:231300), Glaucoma, primary open angle (POAG; MIM:137760), Glaucoma 1, open angle, A (GLC1A; MIM:137750) and Peters anomaly (PAN; MIM:604229). These disorders cause a progressive optic neuropathy characterised by visual field defects that ultimately lead to irreversible blindness. Common mutations causing GLC3A include G61E, E387K, R368H, R390H and R469W (Bejjani et al. 1998, Plasilova et al. 1999, Vincent et al. 2002, Passuto et al. 2010). A loss-of-function mutation causing POAG is P52L (Passuto et al. 2010). A mutation causing GLC1A is V432L (Vincent et al. 2002). Mutations causing PAN are M1T and W57* (Vincent et al. 2001).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
EST17b [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5605147
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
17beta-estradiol
hydron
dioxygen
NADPH(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5605147