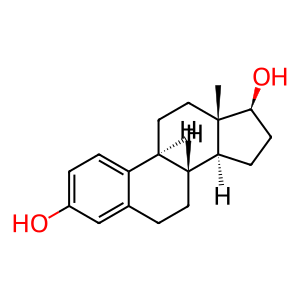
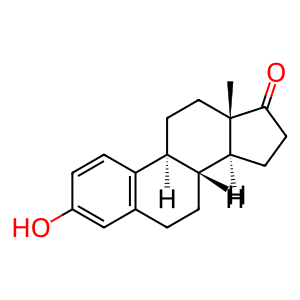
Reaction: HSD17B14 tetramer oxidises estradiol (E2) to estrone (E1)
- in pathway: Estrogen biosynthesis
17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases are primarily involved in the metabolism of 17-hydroxysteroids and of other substrates such as fatty acids, prostaglandins and xenobiotics. The human DHRS10 gene encodes 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 14 (HSD17B14) which in tetrameric form can oxidise estradiol (E2) to estrone (E1) in vitro (Lukacik et al. 2007). It shows highest expression in brain, liver and placenta and has been shown to act as a protective factor in breast cancer (Sivik et al. 2012).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [cytosol]
E1 [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
E2 [cytosol]
NADP+ [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-6810594
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
17beta-estradiol
NADP(3-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
estrone
NADPH(4-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-6810594