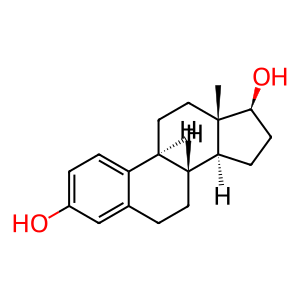
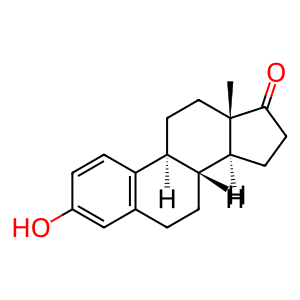
Reaction: HSD17B2 oxidises estradiol (E2) to estrone (E1)
- in pathway: Estrogen biosynthesis
Estradiol 17-beta-dehydrogenase 2 (HSD17B2) is a microsomal enzyme expressed in osteoblastic cells (Wu et al. 1993, Dong et al. 1998). It catalyses the oxidation of highly active beta-estradiol (E2) and testosterone into the weaker 17-ketosteroids estrone (E1) and androstene-3,17-dione, respectively. Osteoporosis is a common, age-related disease characterised by a systemic impairment of bone mass, increasing bone fragility and fracture risk. A drop in E2 and testosterone levels, occurring with ageing, is the main factor driving the onset and progression of this disease. Potent inhibitors of HSD17B2 could be a novel treatment for this disease (Gargano et al. 2015).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [cytosol]
E1 [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
E2 [cytosol]
NADP+ [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8862137
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
17beta-estradiol
NADP(3-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
estrone
NADPH(4-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8862137