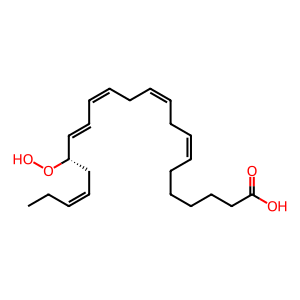
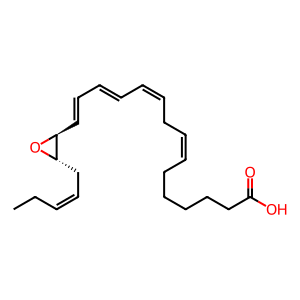
Reaction: ALOX5 dehydrogenates 17(S)-Hp-DPAn-3 to 16(S),17(S)-epoxy-DPAn-3
- in pathway: Biosynthesis of DPAn-3-derived protectins and resolvins
In neutrophils, an unknown lipoxygenase may mediate hydrogen abstraction from 17(S)-hydroperoxy-docosapentaenoic acid (17(S)-Hp-DPAn-3) to form 16(S),17(S)-epoxy-docosapentaenoic acid (16(S),17(S)-epoxy-DPAn-3) (Dalli et al. 2013). If, as assumed, DPA metabolism follows the same path as DHA metabolism, the lipoxygenase could be the dual-functional 5-lipoxygenase (ALOX5). The formation of this epoxy intermediate is supported by chemical synthesis experiments (Aursnes et al. 2014, Primdahl et al. 2017).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
16(S),17(S)-epoxy-DPAn-3 [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
NADP+ [cytosol]
17(S)-Hp-DPAn-3 [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9025999
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
NADP(3-)
(7Z,10Z,13Z,15E,17S,19Z)-17-hydroperoxydocosapentaenoic acid
Reaction output - small molecules:
(16S,17S)-epoxy-(7Z,10Z,12E,14E,19Z)-docosapentaenoic acid
NADPH(4-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9025999