Reaction: nsp14 acts as a cap N7 methyltransferase to modify SARS-CoV-1 gRNA complement (minus strand)
- in pathway: Replication of the SARS-CoV-1 genome
The genomic and subgenomic mRNAs of SARS-CoV-1 coronavirus, including the minus strand genomic RNA complement, are presumed to be capped at their 5′ end, based on studies of the mouse hepatitis virus (MHV) (Lai and Stohlman 1981) and the equine torovirus (van Vliet et al. 2002). The non-structural protein 14 (nsp14) acts as an RNA guanine-N7-methyltransferase (N7-MTase) that completes the synthesis of the cap-0 on SARS-CoV-1 minus strand genomic RNA. The cap-0 represents N7-methyl guanosine connected to the 5′ nucleotide through a 5′ to 5′ triphosphate linkage, and is also known as m7G cap or m7Gppp cap. The N7-MTase domain maps to the carboxy-terminal part of nsp14 (Chen et al. 2009). Cap-0 formation requires three sequential reactions catalyzed by RNA triphosphatase (TPase), guanylyltransferase (GTase), and N7-MTase. There is no evidence that nsp14 possesses TPase and GTase activities, and no other SARS-CoV-1 proteins with these activities have been identified, so the identities of the enzymes that mediate these required steps remain unknown. Based on the study of the human coronavirus 229E, non-structural protein 13 (nsp13) may have a TPase activity in addition to its established helicase activity (Ivanov and Ziebuhr 2004).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
PPi [cytosol]
Pi [cytosol]
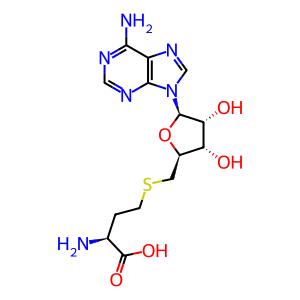
S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine [cytosol]
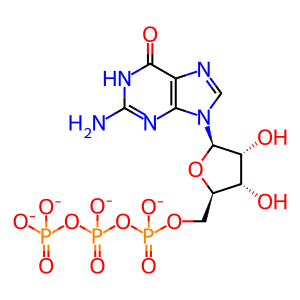
GTP [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
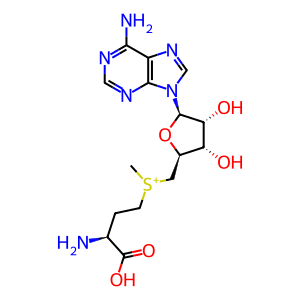
S-adenosyl-L-methionine [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9684018
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
GTP(4-)
water
S-adenosyl-L-methionine
Reaction output - small molecules:
diphosphate(3-)
hydrogenphosphate
S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9684018